Sill-Plate Method
The sill-plate method is the most common form of connection and can be used with either concrete or concrete block foundation walls. It consists of a wood sill plate anchored to the foundation wall (Figure 56) for the support and fastening of the joists and a rim joist attached to the ends of the joists. The sill plate is usually supported on the top of the foundation wall, in which case the bottom of the sill plate should be at least 150 mm (6 in.) above the finished grade, or else it must be separated from the concrete by 0.05 mm (2 mil) polyethylene or Type S roll roofing, or the wood framing must be preservative-treated. A foam gasket should be placed between the concrete and the sill plate to reduce or eliminate air leakage at this juncture.
Where it is desirable to lower the elevation of the main floor in relation to the top of thefoundation, the top of concrete foundation walls may be reduced to 90 mm (31⁄2 in.) in thickness (Figure 57). If siding or stucco is used as an exterior finish, a sill plate anchored to the top of the wall supports the wall framing, and a separate sill plate located on a ledge formed in the wall supports the floor joists.
Where brick veneer is used, the top of the foundation wall supports the brick, and the floor framing supports the wall framing (Figure 58). If the thickness of the wall is reduced, the height of the reduced section cannot exceed 350 mm (14 in.).
Figure 56
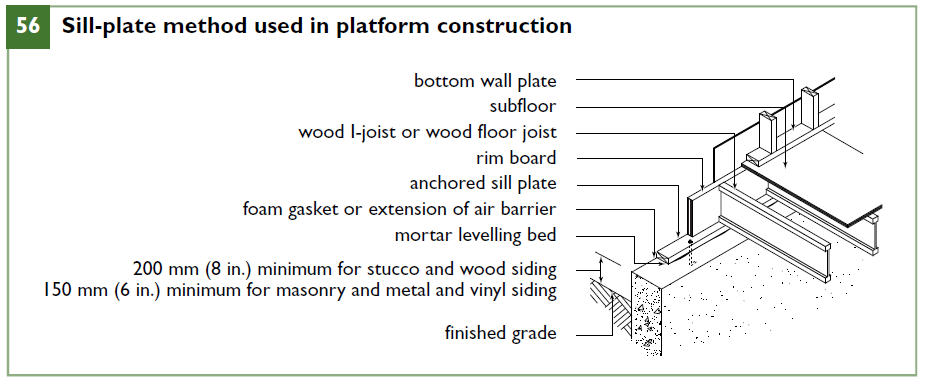
Figure 57
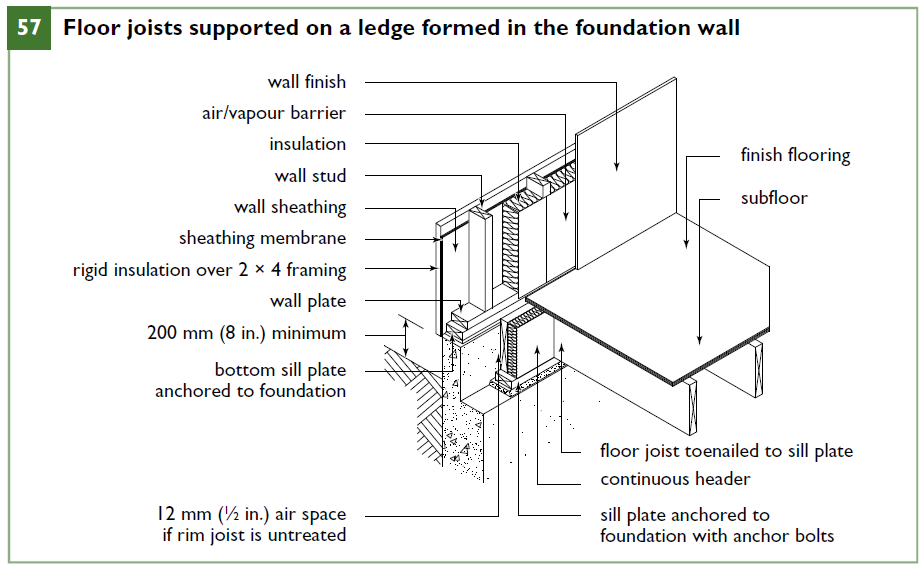
Figure 58

Source : Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC)





